
Atmospheric pressure Wikipedia
Atmospheric pressure, sometimes also called barometric pressure (after the sensor), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth (or that of another planet). The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as mbar (101325 Pa ), equivalent to 760 mm Hg ( torr ), inches Hg , or psi . [1]

PRESSURE
As already discussed, the cistern barometer measures atmospheric pressure because its well is open to the atmosphere and there is zero pressure at the top of the closed tube. The height of the Hg column is a direct measure of pressure (cm or in Hg). The pressure/depth equation can be used to calculate atmospheric pressure in any units.

Pressure Engineering ToolBox
The Standard Atmospheric Pressure is defined at sea level at 273 o K (0 o C) and is bar or 101325 Pa (absolute). The temperature of 293 o K (20 o C) is sometimes used. In imperial units the Standard Atmospheric Pressure is psi. 1 atm = bar = 101.3 kPa = 10 5 Pa = psi (lb f /in 2)= 760 mmHg = mH 2 O = 760 torr = inHg = 1013 mbar = kg f /cm 2 =

Difference Between Gauge and Absolute Pressure Measurement
The simplest way to explain the difference between the two is that absolute pressure uses absolute zero as its zero point, while gauge pressure uses atmospheric pressure as its zero point. Due to varying atmospheric pressure, gauge pressure measurement is not precise, while absolute pressure is

Gauge Pressure, Absolute Pressure, and Pressure
Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to atmospheric pressure. Absolute pressure is the sum of gauge pressure and atmospheric pressure. Aneroid gauge measures pressure using a bellows and spring arrangement connected to the pointer of a calibrated scale. Open tube manometers have U shaped tubes and one end is always open.

Absolute Pressure Calculator Online Calculators
Pressure is the force per unit area applied to an object in a direction perpendicular to the surface. Here we can calculate for Absolute Pressure, Gauge Pressure, Atmospheric Pressure.

Convert in Hg to psi Conversion of Measurement Units
It also gives the correct answer for absolute pressure, assuming you are measuring psia, which is the pressure relative to absolute zero vacuum. If you are measuring relative to vacuum and want to resolve the pressure relative to the atmosphere, then you should use the form below. in Hg (relative to vacuum) psi (relative to atmosphere)

a/c thermodynamics section 3 Flashcards Quizlet
Start studying a/c thermodynamics section 3. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Search. what would our absolute pressure be if our gauge pressure were 60 psig? vacuums, partial vacuums, inches of mercury vacuum 20" HG absolute.

Barometer Wikipedia
When atmospheric pressure is measured by a barometer, the pressure is also referred to as the "barometric pressure". Assume a barometer with a cross sectional area A, a height h, filled with mercury from the bottom at Point B to the top at Point C. The pressure at the bottom of the barometer, Point B, is equal to the atmospheric pressure.

Fundamentals of Vacuum Hydraulics & Pneumatics
To adjust a pump rating, think of that rating as a percentage of atmospheric pressure at sea level. If a pump is rated for 25 , it can achieve 83.4% (25 ) of a sea level perfect vacuum. At a 5000 ft elevation, that same pump can achieve 83.4% of 25 or a vacuum of .

nsthslgy1 Flashcards Quizlet
Thus, there is an approximate 10 cm H2O fluid column from the level of the patient's heart to the transducer. This will cause the pressure reading from the transducer system to read approximately 7.5 mm Hg higher than a true arterial pressure of the patient. A 20 cm column of H2O will exert a pressure equal to 14.7 mm Hg.

Understanding Vacuum Measurement Units Vacaero
Mercury vacuum gauges. This simple gauge measures the difference in the levels of the mercury from 0 inches at atmospheric pressure up to inches of Hg at the best vacuum attainable. This scale is still in use today, usually shown as 0 to 30 inches of Hg on gauges such a Bourdon dial gauges.

a/c unit 8 Flashcards Quizlet
a/c unit 8. STUDY. PLAY. Convert a reading of 20" Hg vacuum to psia. Vacuum is any pressure less than atmospheric pressure. It is measured using mercury columns. Mercury columns measure how much pressure has been removed. Define vacuum and tell how it is measured.

How to Calculate Tank Level Using Pressure Hunker
Define the level application. In this example, a pressurized water tank with a specific gravity of has two accurate zero to 10 psi pressure gauges, one at the top and one on the bottom. If the top one reads 4 psi, and the bottom one 7.5 psi, you can calculate the level from the pressure difference.

terminology Gauge pressure vs. absolute pressure
Absolute pressure is zero referenced against a perfect vacuum, so it is equal to gauge pressure plus atmospheric pressure. Gauge pressure is zero referenced against ambient air pressure, so it is equal to absolute pressure minus atmospheric pressure.

Measuring vacuum with negative gauge or absolute ranges
Help Converting negative gauge to absolute pressure. What is bar and its conversion to a “positive” bar value? It looks like a negative gauge value (suction/vacuum) so it can only be described as a positive value if measured as an absolute referenced value with respect to a perfect vacuum.

Pressure Calculation for Manometers eFunda
Small pressure differences, such as those experienced in experimental wind tunnels or venturi flowmeters, are measured by lighter fluids such as water (27.7 inch H 2 O = 1 psi; 1 cm H 2 O = 98.1 Pa). To calculate the pressure indicated by the manometer, enter the data below. (The default calculation is for a water manometer with a 10 cm fluid column, with the answer rounded to 3 significant figures.):

Thermodynamics Solutions Manual: October 2014
1 40 A vacuum gage connected to a chamber reads 35 kPa at a location where the atmospheric pressure is 92 kPa. Determine the absolute pressure in the chamber.

Pressure, Barometers, & Barometric Pressure Challenger
Atmospheric pressure (same as barometric pressure) varies somewhat on a day to day basis. When the readings are taken over a long period of time in many different locations and then averaged, it is found that the average pressure at sea level is very nearly 76 centimeters (cm) of mercury.








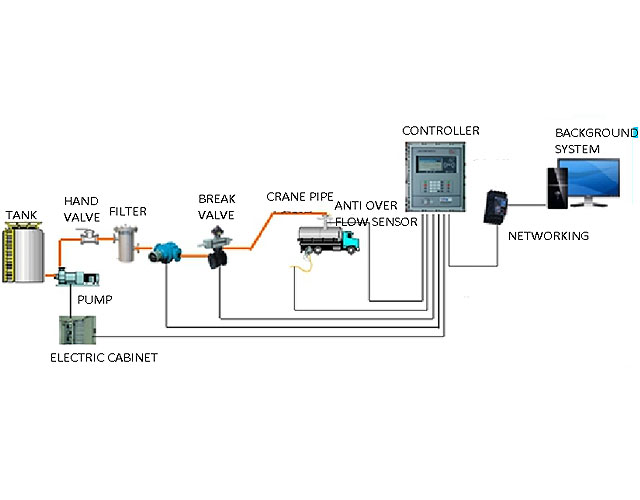
 Message
Message tel
tel Inquiry
Inquiry